What Is the Tolerance of a Laser Cut Hole?
The tolerance of a laser cut hole can be as tight as just a few microns to +/- 0.002” mils (0.0508mm), in many instances. The variance of course is subject to factors such as the laser cutting machine used, material cut, and the geometric path the laser will travel. Hole sizes, especially in micro-machine manufacturing, are a constant variable that mechanical engineers and product designers inquire about. Micro sized holes are features that may be subjected to fluid and gas transmission or possibly light or sound. At extremely small sizes, the difference in diameter can be critical affect the performance of an intended device. Holding a specified tolerance is the challenge of laser cutting service providers and from experience consider and adjust to several factors during the manufacturing process.
Challenge Accepted
All lasers cut features to a designed tolerance of size and edge quality. Holes and for this discussion, round holes are common for many devices and micro-machining needs. As mentioned earlier, small round holes are designed to regulate volumes of fluids, gases, sound waves or other substances and particles. For a laser manufacturing, the first of many details that are reviewed will be the geometry to cut and the material and thickness being requested. The combination of these will direct to which laser technology has that right capability to achieve the intended design. For example, laser cutting 1mil thick copper foil, with holes in diameter of 4mils or 0.1016mm, and a tolerance of +/- .0005” mils (0.0127mm), will cut extremely well on an ultraviolet laser system. On the other hand, a project cut on a 20mil thick copper sheet, with holes diameters of .005” mils (0.127mm) to .015”mils (0.381mm), will have a tolerance of +/- .002” to .003”mil (0.0508 to 0.0762mm). The given tolerance of laser cutting technology is consistent within the chosen laser system. This reliability is controlled in part through industry quality standards like ISO, which is the International Organization for Standardization. It is a non-governmental organization, compromising standards from over 160 countries. Laser manufacturing service providers, specializing in micromachining, undergo ISO certification and input processes to ensure the laser cutting machines operate to their potential.

How Small of a Hole Can a Laser Cut?
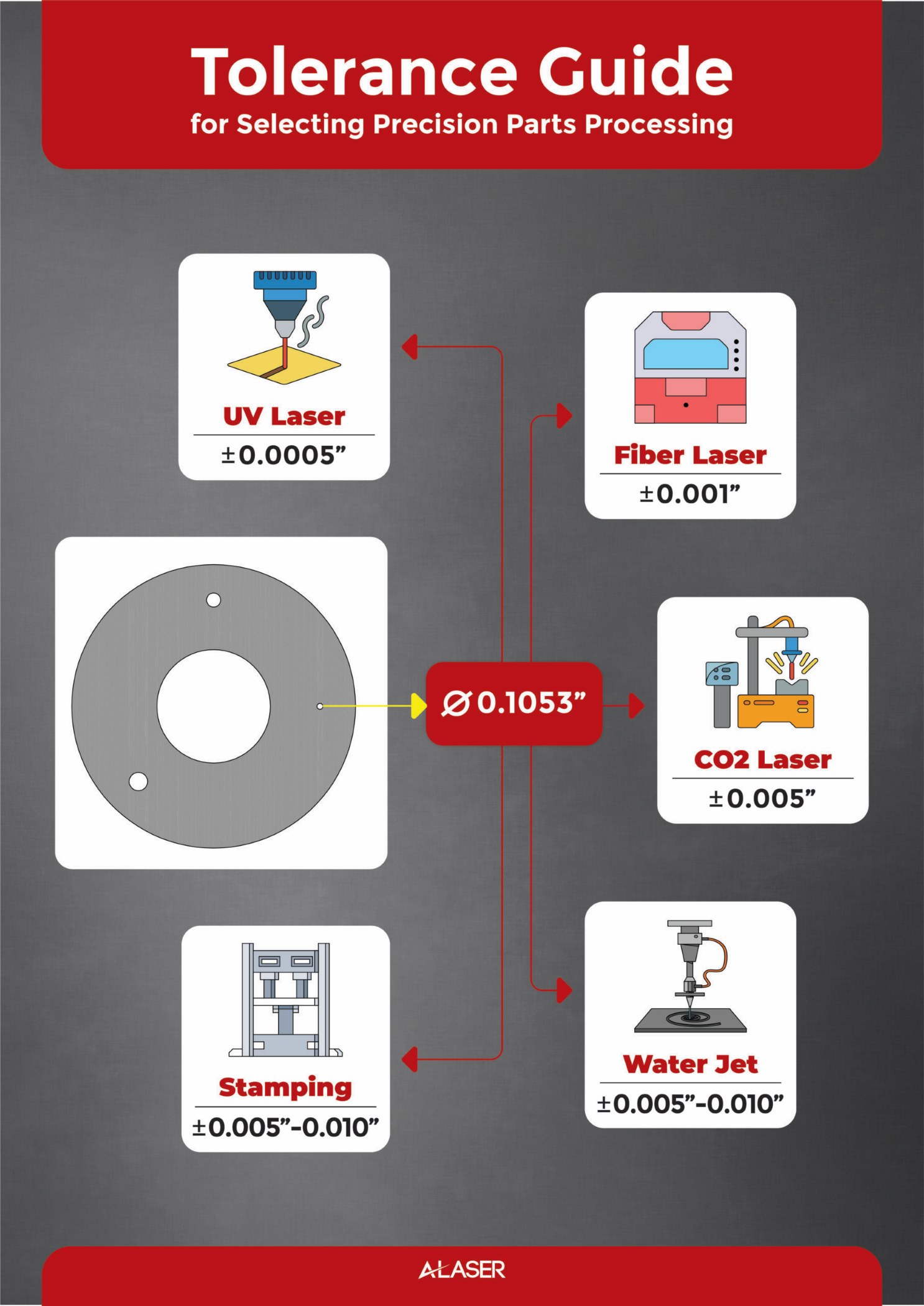
A recurring question asked of laser manufacturers is “how small of a hole size can you cut?” The answer would be brief if there was only one laser technology available. Fortunately, laser technology is diverse and serves many industries with machines that can cut a wide range of materials. The type of laser systems in use today can handle the demands of innovative engineers who wish to push beyond what is currently the mainstream. The diameter of precision cut holes is dependent primarily on the material being cut and the laser method being used. The following list can be used as a guide to direct the type of laser system or systems available for the smallest hole diameters and tolerance you may need:*
- UV or Ultraviolet Laser: Theoretically with beam diameters of 20micron, a hole can be cut to this size. Materials will need to be ultra-thin from about 0.0127mm to 0.0508mm thick, with tolerance possible of +/- 0.0127mm to 0.0254mm.
- IR or Infrared Laser: A typical system may have a beam diameter of 35micron; therefore the smallest hole will be about 0.040mm, at material thickness of 0.254mm and tolerance of +/- 0.0254mm to 0.0508mm.
- Fiber Laser: Some fiber laser and other laser systems may have dual laser heads. An example of this is one head at 18micron diameter, and another at 35micron diameter. The smallest hole will depend on the materials’ thickness and geometry. Fiber lasers generally are more robust and cut thicker metal alloys from 0.254mm up 4mm thick or thicker. Tolerance expectation is +/- 0.0254mm to 0.0762mm.
- Femtosecond Laser: Used in micro-machining femtosecond laser can produce hole diameters ranging from 0.5micron to 25micron, with tolerances of +/- 0.00254mm to 0.0127mm.
- CO2 Laser: CO2 laser excel at cutting plastics, paper, wood and even metals depending on the power of the system. Generally, the smallest hole size achievable on CO2 lasers is paired to the thickness being cut. A 1mm thick plastic will cut a minimum 1mm hole, with a tolerance of +/- 0.127mm.
*The above-mentioned laser systems have numerous variants of laser technologies that encompass levels of wattage and pulse rates that effectively give a broad range of capabilities. Further investigation and communication with laser technology specialists will aid in sourcing the best laser cutting machine for your project.
Conclusion
The tolerance of a laser-cut hole is contingent upon the type of laser system employed, the material being cut, and its thickness. Each laser system, whether it be UV, IR, fiber, or femtosecond, brings unique capabilities and precision levels to the table. The characteristics of laser technology, material properties, and desired hole diameters shape the outcome of precision micromachining. Understanding these factors is essential for achieving optimal results. If you’re considering a laser cutting project and wish to explore the best solutions tailored to your specific needs, I invite you to engage with our team of experts. Let us guide you towards the most effective technology, ensuring your project is executed with unparalleled precision and excellence.
