Revolutionizing Precision: The Power of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting machines are tools so precise, they can cut through steel with the delicacy of a surgeon’s scalpel. A tool that can transform raw materials into intricate designs, from delicate medical device components to robust industrial brackets. This is the power of laser cutting technology, a revolutionary advancement that has reshaped industries worldwide. Laser cutting machines are today integral to many manufacturing sectors and integrated for volume manufacturing and R&D and prototype functions.
The Birth of a Precision Instrument
The journey of laser cutting began in the mid-20th century with the development of lasers. Scientists harnessed the power of light to create intense beams capable of cutting, engraving, and welding materials. After World War II, technical progress was hindered by current methods of that time. Laser cutting machines, though much cruder than today’s technology, opened the door. By focusing light energy onto a specific point, laser cutting machines can precisely vaporize material, leaving clean, precise cuts.

The Harnessing of Light Energy
Light is used to cut materials. That’s pretty cool and fascinating when you think about it. Laser systems do not use “white” light, that we experience in everyday living. Light is made is numerous wavelengths and those like ultraviolet, for example, are amplified and focused to form powerful beams of light energy. Using light energy coupled with sophisticated system of components, is the heart of a laser cutting machine Over the past 50 years, the advancements in electronics has increased capabilities of laser technology to control aspects such as:
- Laser Source: This generates the high-powered laser beam, which can be made from light wavelengths of ultraviolet, CO2, picosecond, femtosecond and fiber as the most common.
- Optical System: This focuses the laser beam onto the material to be cut. Using lenses, mirrors and crystals, the laser beam is focused.
- Motion Control System: This precisely controls the movement of the laser beam, ensuring accurate cuts. Many laser systems work in an x and y axis, whiles there are some operating in 3,4 and 5 axes.
- CNC Controller: This computer system directs the entire cutting process, interpreting design files and controlling the machine’s movements. Computer numeric control continues to advance in parallel with technology. As faster processors are developed and smarter sensors used, CNC controllers tie the laser process together.
By understanding the science behind laser cutting, we can appreciate the incredible capabilities of this technology and its impact on modern manufacturing.
Why Laser Cutting Matters
Laser cutting technology offers a multitude of advantages by having characteristics such as:
- Unparalleled Precision: Laser cutting machines can produce intricate designs with exceptional accuracy and hold tight tolerances far surpassing traditional cutting methods.
- Versatility: From thin sheet metal to thick steel plates, laser cutting can handle a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
- Efficiency: Laser cutting is a highly efficient process, capable of cutting multiple parts simultaneously and reducing production time.
- Clean Cuts: Laser cutting produces clean, burr-free edges, eliminating the need for additional finishing processes.
- Complex Designs: Laser cutting can handle complex shapes and intricate details that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
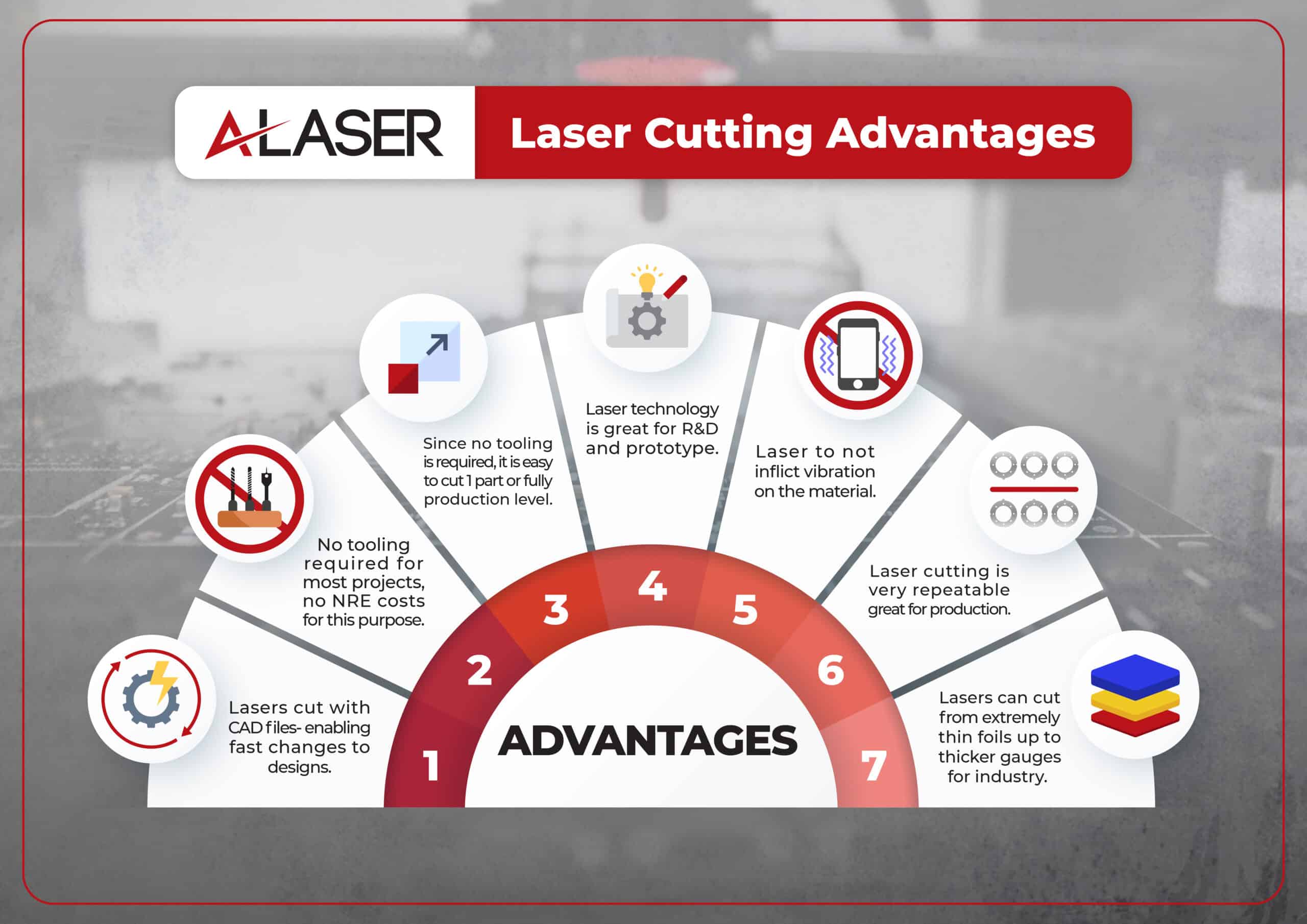
What Can You Expect to See?
Manufacturing using a laser cutting machine is much different than other methods, which can be very surprising to visitors for the first time. Unlike CNC manufacturing, there are no external tools to be used. The vast assortment of spindles one would see at a CNC shop is not present in a laser manufacturing facility. Nor is there any excess of debris or coolant fluids. Laser “tools” are produced by adjusting parameters of the laser system and data such as power or wattage, focus of the beam, cut rate, dwell time, laser passes, and frequency to name a few. Laser cutting machines use ablation to cut. The energy imposed onto the material is obliterated, there minimal debris is left over. Many systems operate with sound levels much lower than stamping, die-cutting and CNC Milling. You could walk by some systems and be indicated of operation only by the laser light moving (which is shielded for safety). With many sensitive projects being processed, laser technology provides the platform to manufacture a precision part by a process that is cleaner than many other methods.
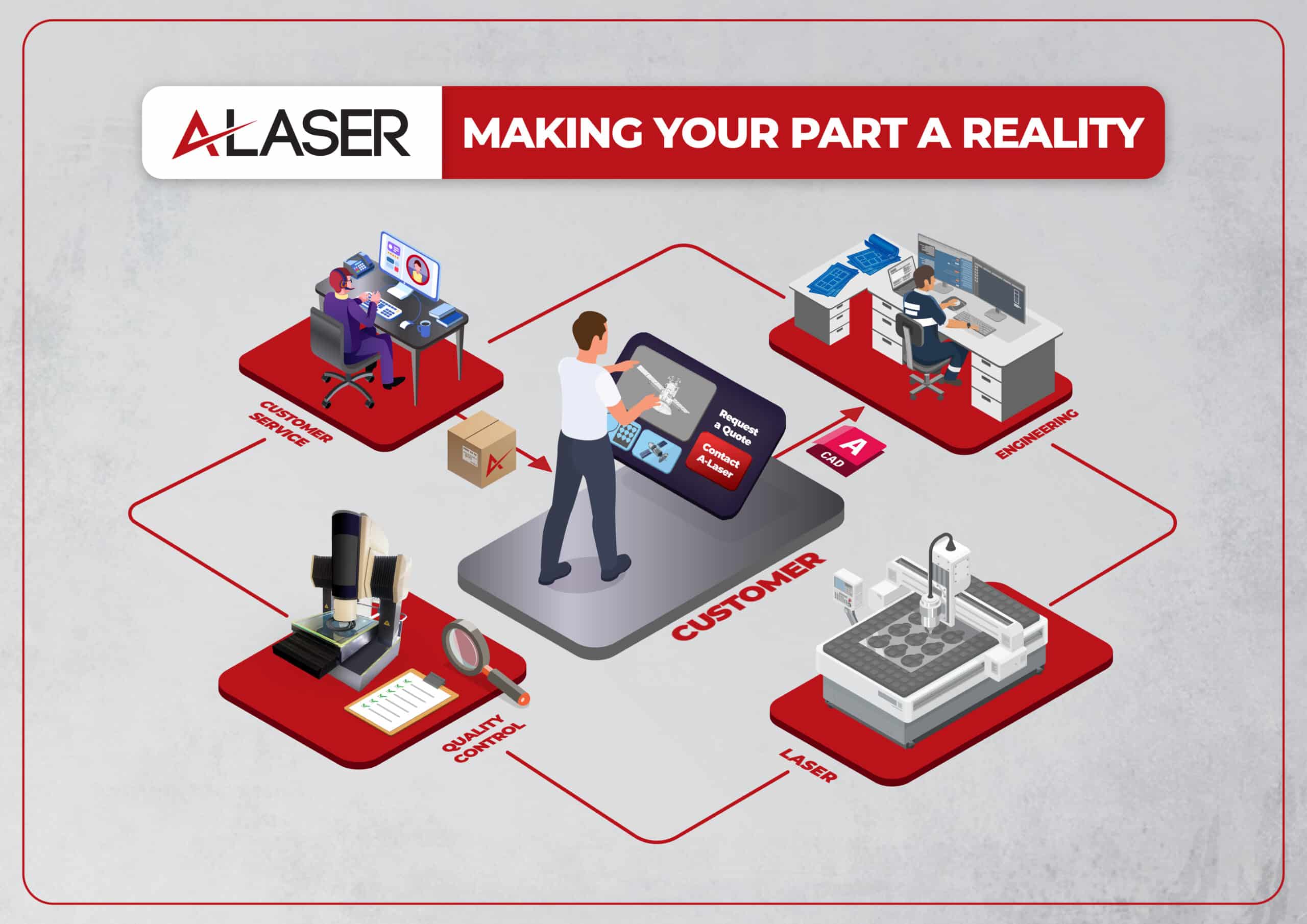
Conclusion
Laser cutting machines are made for different uses and the precise cutting of different materials. For the ultra-thin materials between 0.0127mm to 0.127mm, one might be using a picosecond, femtosecond or ultraviolet laser. For thicker metal foils, a manufacturer may use an infrared or fiber laser system. For plastics, a CO2 laser will be a good choice. Will these laser technologies, there is a similarity between them in their flexibility to process short runs or support full long term volume manufacturing. Laser systems do not incur much NRE costs, nor do they need extensive and expensive tooling. They operate under conditions much differently from other methods and prevent delicate materials from damage during the laser process. They range in size from tabletop units that are favored by hobbyists to larger industrial systems with footprints measured in meters rather than inches. Further capabilities and services of laser cutting machines will be found throughout this website. These precision tools are often used as an asset to a much larger supply stream providing high quality and precision support where other methodology cannot.
