Choosing the Best Plastic For the Job
Laser engraving of plastic is a method used to add valuable product information like signage, logos, barcodes, unique 2D codes, and countless other information onto products. The laser engraving results in added traceability and identification, as well as product names for branding and aesthetic appeal. For manufacturers producing a new plastic product that requires durable and customizable engraving, what plastic material and laser technology do they use? Laser engraving, with its precision and versatility, is an obvious choice for adding intricate patterns, part identification and branding. However, the vast array of plastic materials available can leave one overwhelmed. The right choice would not only impact the product’s aesthetics but also its functionality and longevity. With laser engraving technology available in various systems, it is best to determine the perfect material for any plastic engraving project.
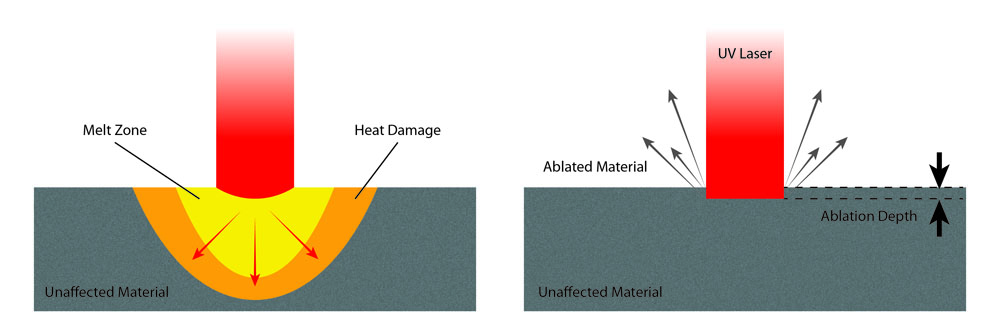
Laser engraving works by utilizing a focused beam of light to remove material from the surface. This process, known as ablation, occurs when the intense energy of the laser beam heats the targeted material, causing it to vaporize or melt. The precision of the laser beam allows for intricate designs and detailed patterns to be etched onto a variety of materials, including plastics. Plastics can be broadly classified into two main categories such as thermoplastics, which plastics soften when heated and can be reshaped multiple times and thermosetting plastics, in which these plastics harden irreversibly when heated and cannot be reshaped. Thermoplastics make up most like materials that are used for laser engraving. The following table shows the most commonly laser engraved plastics:
| Plastic | Why Used in Products | Applications | Laser Technology Used to Engrave | Expected Edge Quality When Engraved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic- Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) | Ideal for applications requiring clarity, durability, and ease of engraving. | Signage, display cases, awards, trophies | CO2, Fiber, Ultraviolet (UV), Femto Second | Typically produces clean, smooth edges with minimal burrs. |
| ABS- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | Suitable for strong, rigid parts and housings, especially in industrial and automotive applications. | Medical industry, Automotive, aerospace, consumer products | CO2, Fiber | Can produce clean edges but may have slight burrs or roughness depending on engraving depth and power. |
| Polycarbonate- (PC)-these contain carbonate groups in chemical structure. | Excellent choice for applications demanding impact resistance and toughness, such as safety shields and helmets. | Safety shields, helmets, automotive parts, medical industry, consumer products, food industry | CO2, Ultraviolet (UV), Femto Second | Generally, produces clean edges, but may have a slightly rougher finish than acrylic. |
| Nylon – Family of synthetic polymers. | A versatile option for flexible, durable parts with good chemical resistance. | Gear parts, housings, prototypes, medical industry, automotive | CO2, Fiber | Can produce clean edges, but may have some burrs or roughness, especially for deeper engraving. |
| PET (Mylar)- Polyethylene terephthalate | Lightweight and recyclable, making it suitable for packaging and signage applications. | Automotive parts, containers, toys, medical use. | CO2, Ultraviolet (UV) | Typically produces clean edges with minimal burrs. |

Additional Factors To Consider When Choosing Plastic for Laser Engraving
- Material properties: The desired properties of the finished product, such as strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
- Laser compatibility: The ability of the plastic to interact with the laser beam effectively, ensuring a clean and precise engraving.
- Engraving depth: The desired depth of the engraving, which can vary depending on the plastic type and laser parameters such as power, beam diameter, wavelength, speed, and focus.
- Surface finish: The desired surface finish of the engraved plastic, whether it should be smooth, matte, or textured.
- Cost: The cost of the plastic material and the laser engraving process.
- Availability: The availability of the plastic in the desired quantities and qualities.
- Processing: The suitability of the plastic. Some plastics are better for laser engraving, as indicated. Other Plastics can melt and not ablate readily to form clean and accurate text or images.
- Regulatory Compliance: This applies to manufacturers providing laser engraving or laser cutting services. Quality Management systems like ISO-9001 series provides guidelines that manufacturers adhere to and use to support in following regulations and standards, such as FDA regulations for medical devices or REACH regulations for chemical substances.
Plastics are made from chemical processing and therefore manufactured under strict regulatory restrictions. Caution needs to be taken when laser engraving plastics like ABS, as harmful fumes can result requiring a fume extractor system to be in place. This oversight, keeps employees from harm during the engraving process, prevents caustic fumes from the environment and makes plastic products safe for consumer use. By carefully considering these factors, the most suitable plastic can be chosen for your laser engraving project and achieve the desired quality results.
Advantages and Benefits of Laser Engraved Plastic
With laser engraving of plastics, the options for manufacturers to produce the type of imagery and product information are clear. Laser technology has advantages over other engraving methods like mechanical engraving and chemical processes such as:
- Precision and Detail: Laser engraving can achieve exceptional levels of precision and detail, allowing for intricate designs and fine lines that are difficult or impossible to replicate with other engraving methods. QR codes, barcodes both need precise definition.
- Versatility: Laser engraving can be used on a wide variety of plastics, to produce shallow or deep engravings. This versatility makes it suitable for a variety of applications.
- Speed: Laser engraving is a relatively fast process, especially compared to manual methods. This can significantly improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
- Non-Contact Process: Plastics are prone to scratches and marring, so by using laser engraving this minimizes the risk of damage or distortion to the workpiece.
- Customization and Iteration: Laser engraving allows for highly customized designs and can rapidly produce several iterations for review, before a confirmed style and setting is approved.
- Automation: High-volume production, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs, are a benefit of using laser machines.
- Durability: The markings created by laser engraving are permanent and resistant to fading or wear, ensuring long-lasting results.
- Clean Edges: Plastics used in laser engraving typically produce clean edges, without the need for additional finishing processes like polishing. This can save time and reduce costs.
- Consistency: Laser engraving of plastics can provide consistent results, ensuring that each engraved piece meets the same quality standards. This is particularly important for mass production applications.
These advantages make laser engraving a preferred choice for manufacturers, supporting all industries.
