Standard Tolerances
Laser Cutting Tolerances: Achieving Precision Across Materials
Laser cutting, with its focused beam of light, revolutionized fabrication by offering unmatched precision and versatility. But how precise is it exactly?
What is cutting tolerance? Understanding laser cut tolerances (the allowable variation in cut dimensions) is crucial for anyone working with laser-cut materials, from plastics and acrylic to metals and alloys. Laser cutting is known for its exceptional accuracy, delivering tight laser cut hole tolerance with minimal deviation from the desired dimensions, or very tight tolerances. Ensuring the quality and consistency of parts for your project is a high priority. Here, we delve into the world of laser cutting tolerances, answering common questions and providing valuable insights.
How accurate is laser cutting?
Laser cutting outshines traditional cutting methods in terms of accuracy and precision due to its non-contact nature and ability to produce finer details. Mechanical cutting methods often result in greater tolerances and may introduce distortion due to physical force, while plasma cutting can lead to wider kerf widths and heat-affected zones. Laser cutting, on the other hand, achieves consistently tight tolerances and minimal heat distortion, making it the preferred choice for applications demanding the highest levels of accuracy and precision.
Laser cutting technologies have evolved significantly, each offering unique advantages and capabilities tailored to diverse applications. Let’s compare them:
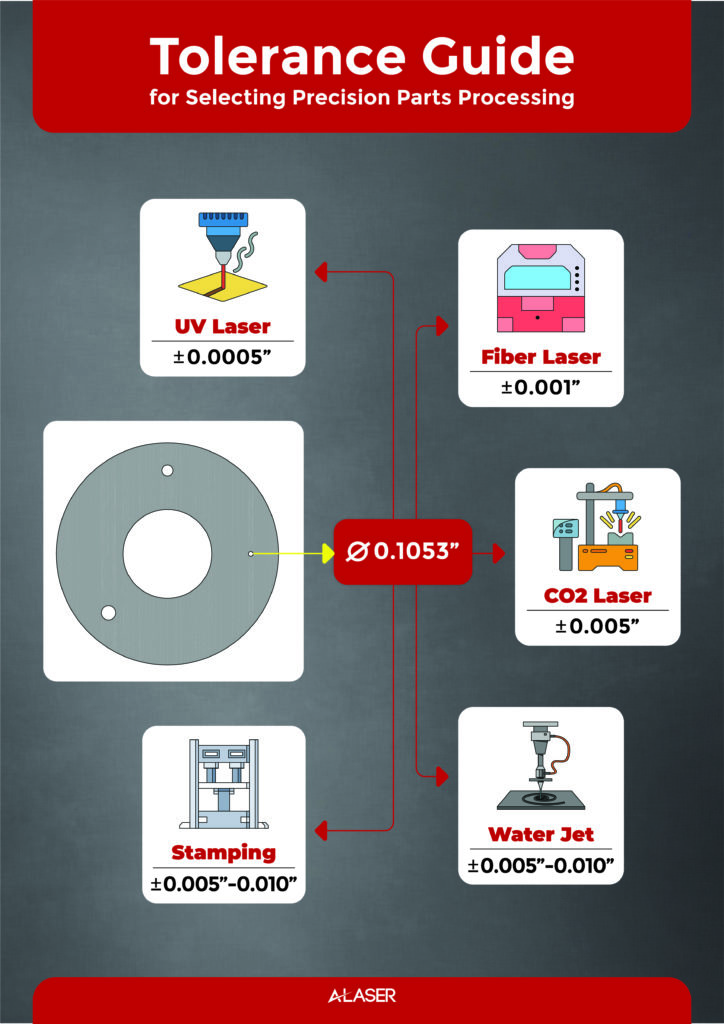
CO2 Lasers: Renowned for their versatility, CO2 lasers excel in cutting non-metallic materials such as plastics, wood, and acrylics. While CO2 lasers offer respectable accuracy levels, typically achieving laser cut hole tolerances ranging from ±0.002 to ±0.005 inches, they may not match the precision of other laser types in certain applications.
Fiber Lasers: Harnessing the power of fiber optics, fiber lasers have revolutionized metal cutting with their exceptional speed, efficiency, and precision. Fiber lasers boast superior accuracy, consistently delivering tight tolerances ranging from ±0.001 to ±0.003 inches. This level of precision makes fiber lasers the preferred choice for demanding metal fabrication projects where accuracy is paramount.
UV Lasers: Ultraviolet (UV) lasers represent the pinnacle of precision, offering unparalleled accuracy and resolution in micro-machining applications. With their short wavelengths and ultra-fine beams, UV lasers achieve astonishingly tight tolerances, often reaching levels as low as ±0.0001 inches. This exceptional accuracy makes UV lasers indispensable for cutting and engraving delicate materials with sub-micron precision.
What is the typical tolerance of a laser cut?
The achievable tolerance in laser cutting depends on several factors, including the type of laser used and the material being cut. Here’s a breakdown of the typical tolerance range for different laser cutting scenarios:
- General Applications (wood, acrylic, plastics): +/- 0.005″ (0.127 mm) to +/- 0.010″ (0.254 mm)
- Tighter Tolerance Applications: With advanced laser technology and expertise, tolerances as low as +/- 0.0001″ (0.0025 mm) can be achieved on some materials.
The typical tolerance of a laser cut can vary depending on several factors, including the material being cut, the thickness of the material, and the complexity of the design. Generally, laser cutting tolerances can range from ±0.005 inches to ±0.010 inches for metals and ±0.001 inches to ±0.005 inches for non-metals. At A-Laser, our standard laser cutting tolerance that we can achieve cutting accuracies down to ±0.0005 inches on most laser cutting materials within our capabilities.
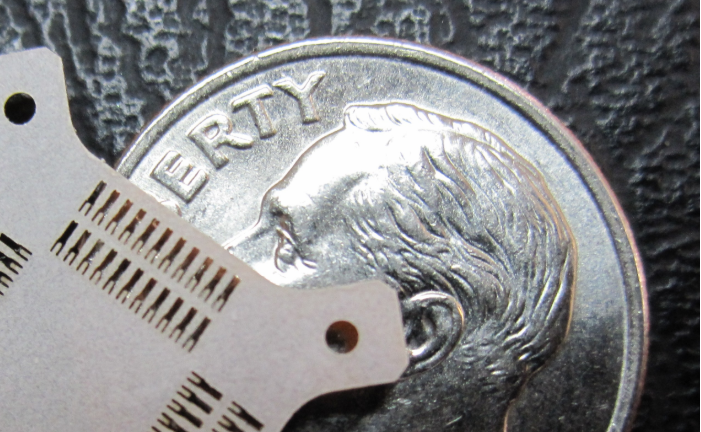

What is the cut tolerance for metal material?
Laser Technology: CO2, Fiber, and UV lasers offer varying levels of precision, with UV lasers reaching tolerances as low as +/- 0.0005″ (0.013 mm) for certain metals. When it comes to metal materials, laser cutting tolerances are typically tighter compared to non-metals. The cut tolerance for metal materials can range from ±0.005 inches to ±0.010 inches, depending on the type of metal being cut and the thickness of the material.
For metal fabrication, achieving high precision is even more critical. Metal’s unique properties require specialized laser cutting techniques.
Here’s a deeper dive into standard laser cutting tolerances for metal:
- Metal Thickness: Thicker materials generally experience slightly larger variations due to heat dissipation during cutting.
- Metal Type: Different metals react differently to the laser beam, impacting the cut edge and achievable tolerance.
- Laser Technology: CO2, Fiber, and UV lasers offer varying levels of precision, with UV lasers reaching tolerances as low as +/- 0.0005″ (0.013 mm) for certain metals.
What is the cut tolerance for plastic material?
Standard laser cut tolerances of plastics will vary depending on the laser technology used, the material, the thickness, and other requirements of the project. As there is not one specific tolerance that can be held, but we can review what are standards and what variables can affect these. The table below is a general guideline for material thickness:
| Material Thickness | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Up to 0.5 mm | +/- 0.05 mm |
| 0.5 mm - 2.0 mm | +/- 0.1 mm |
| 2.0 mm - 5.0 mm | +/- 0.15 mm |
| 5.0 mm - 10.0 mm | +/- 0.2 mm |
| 10.0 mm and above | +/- 0.3 mm |
The guideline is broad because like many industries, there are multiple elements that influence a level of tolerance in manufacturing including laser technology. Laser cutting technology comes in many forms like ultraviolet, CO2, infrared, and fiber technology. Each of these system types has different power levels and beam diameters, but out of these four mentioned only ultraviolet and CO2 lasers will have the capability to laser cut plastics. One example is when approached by a medical device OEM, (Original Equipment Manufacturer), they had done some prototyping with a CO2 laser. The produced parts allowed them to see the possibilities of their design, but the tolerance held was holding back progress. They needed a system that would keep them moving forward by holding a tighter tolerance. Using an ultraviolet system gave them the tolerance required. A better understanding of laser cut tolerance for plastics is to know what additional factors influence the final manufactured component.
Tolerance is calculated with the formula: K x D
- (K) is a coefficient that depends on material properties, laser cutting machine performance, and cutting parameters.
- (D) represents the design dimension requirement.
Additional factors involved are:
- Laser Accuracy: Ultraviolet laser systems can come with beam diameters of 20um micron. This gives the ability to hold smaller features but also hold tighter tolerances. CO2 laser systems can have beam diameters of 100um microns.
- Material properties: Materials have different properties like thermal conductivity, melting point, pliability, and machinability. The thickness will affect the laser cutting and the tolerance that can be held.
- Laser Power: Lasers, like ultraviolet and CO2, come in various levels of power that is indicated by wattage. For example, an ultraviolet laser with a maximum wattage of 16watts and beam diameter of 20um micron can cut plastic materials within a tolerance of +/- .001” to +/- .003” mills. For a CO2 laser of 50 watts of power cutting the same material but with a larger beam of 100um micron or .004” mills, would not have the advantage of holding the same tolerance. On the on the other hand a CO2 laser of 50 watts will be able to cut thicker plastics but at a tolerance of +/- 100um to 300um, while the ultraviolet would not be able to process the thicker grade of plastic material. Laser power and other systems capabilities will influence what laser cut tolerances can be held.
Laser cutting tolerances of plastics will be determined by the project’s requirements of material and thickness, geometry, and the type of laser systems used. Communication with a qualified service provider will focus on the best approach to fulfill the requirements for your next precision laser cut part.
