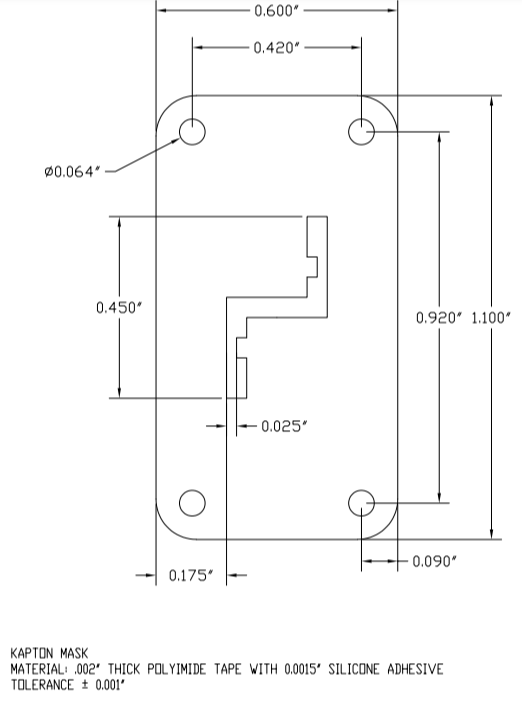
Laser Cut Upilex Service
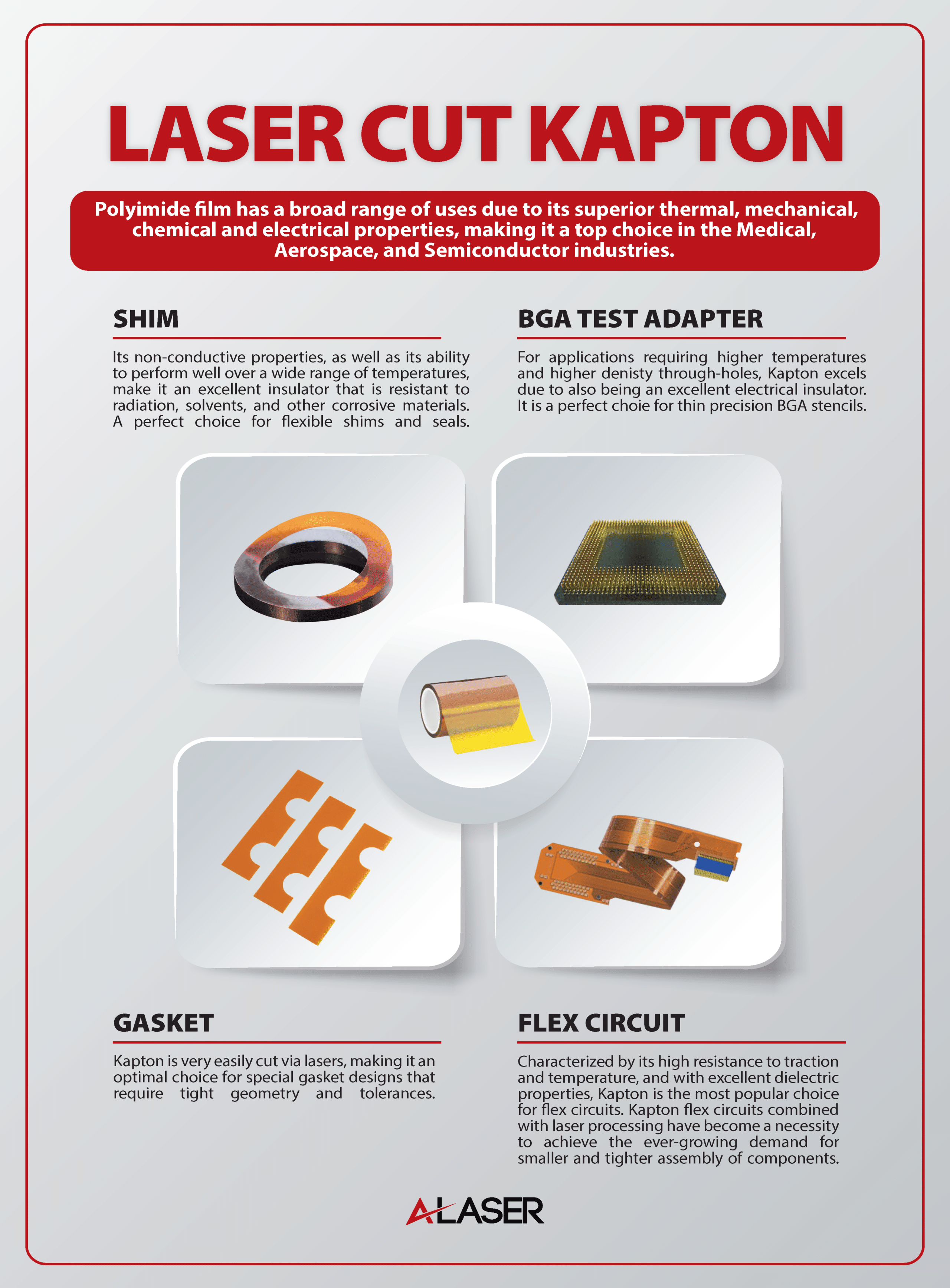
A long-term success story of laser cutting technology has been the manufacturing of precision flat components made from polyimide. With continued advancements from materials manufacturers, polyimides are being used in countless ways that affect our lives in so many positive ways. You will find polyimides in consumer goods as flexible circuits to aerospace use as insulation for high temperature wiring and cable wrapping. Polyimides in general have shown their chemical and thermal resistance for such uses. As technical advancements have come forward in developing new types, Upilex, which was developed by UBE Corporation, has been a key factor in critical technologies. This ultra-high temperature resistant material that exhibits extreme durability can be transformed through laser cutting into complex precise geometries. Additionally, components made with Upilex, have unmatched chemical resistance and superior mechanical strength, that other polyimides cannot match. To support the ongoing needs of technology, laser cutting is a favored partner for many applications and industries. To learn more about how laser cutting of Upilex can potentially support your project, the following Q&A have been provided.
Precision of Laser Cut Upilex
What Are the Tightest Tolerances Your Laser Cutting Process Can Maintain When Cutting Upilex?
UV lasers cut polyimide through a process called photoablation, which breaks the molecular bonds of the material directly with minimal heat. This non-thermal cutting mechanism is key to maintaining ultra-tight tolerances of +/- .5mls to +/- 1 mil for many of the applications we see. As Upilex get thicker at about over 10 mils thick, you may see tolerances of +/- 2mils. The intricacy and complexity of the features will also affect tolerance.
Laser Cutting Versus Other Methods
How Does Laser Cutting Compare to Die-cutting, Waterjet, or CNC Machining of Upilex?
Laser Cutting (Best for Intricacy & Flexibility)
Laser technology offers the highest level of precision and the narrowest kerf at about 20micron, especially when using UV lasers on thin polyimide film. It produces a very clean edge; however, lasers can cause a minor Heat Affected Zone (HAZ), leading to slight charring or discoloration on the polyimide edge. With no tooling makes it ideal for prototypes and low-to-medium volume, intricate production runs
Die-Cutting (Best for High Volume)
Die cutting precision is good but limited by the physical die and generally less accurate than laser or waterjet cutting. The Edge Quality provides clean cuts, but the mechanical shearing force can introduce a slight “toe” or “heel”, a minor distortion, on the edge. There is no HAZ/Thermal: Zero HAZ as it is a cold, mechanical process. Requires a high initial investment in a custom die, but once the die is made, the per-part cost is the lowest, making it the fastest and most economical option for millions of parts.
Waterjet Cutting (Best for Zero-HAZ)
Waterjet cutting accuracy is very high, approaching laser accuracy, but typically with a wider kerf. With waterjet you can expect edges that are smooth with absolutely zero thermal effects (HAZ), making it a safe choice for heat-sensitive materials like Upilex, where the retention of material properties is critical. However, for cutting films, this method will be slower than laser cutting for thin films, which can increase the per-part cost for low-volume production.

CNC Machining (Routing) (Best for Thicker Material)
CNC machining accuracy is very high, suitable for tight tolerances. The surface finish is good, though the process involves mechanical forces and requires parts to be held by tabs, which must be manually removed and deburred later. Regarding Upilex, while technically possible, CNC routing is rarely used for thin polyimide films as it is primarily designed for cutting thicker plastics, composites, or 3D geometries that film materials are not suited for.
Factoring Characteristics
How Do Material Characteristics Like Reflectivity, Softness, or Thermal Conductivity Affect Edge Quality and Tolerance Control in Upilex?
When laser cutting any material, the characteristics of each will be considered and parameters adjusted according to how the laser reacts. For Upilex, using an ultraviolet, picosecond or femtosecond laser is best. Reflectivity of this polyimide is generally not a concern. Upilex has low thermal conductivity, so heat does not dissipate quickly. Laser power needs to be adjusted to minimize HAZ. Softness of Upilex gives it pliability so it must be kept flat during the cutting process. This is done with vacuum control systems and results in very accurate component features.

Cutting Upilex
What Edge Quality Can Be Expected When Laser Cutting Upilex? Are Burrs or Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ) Present?
With the characteristics of high mechanical strength and high thermal threshold, the laser cut edge of a Upilex component will stand up to stringent specifications. This does come with experience and knowledge of laser cutting such a material. By adjusting parameters such as the laser power, laser frequency, laser passes, and laser focus, preventing or minimizing HAZ is done. Burrs are generally not seen on laser cut polyimides unless the forementioned parameters are not controlled.

Key Takeaways
What Are the Benefits of Laser Cutting Upilex?
The benefits of any manufacturing process can be summarized by highlighting the capabilities of the chosen method. This is true for laser cutting, especially as a manufacturing process to produce precision components out of Upilex. The capabilities of using laser technology go beyond the precise cut parts. Laser cutting offers design freedom for micro-features that are impossible to achieve with the mechanical limitations of a physical die-cut tool and avoids the mess and material warping risks associated with waterjet cutting or the slow speed of CNC milling. Ultimately, laser cutting is the chosen method because it not only produces the most accurate part but also preserves the intrinsic value and high-performance characteristics of the Upilex film itself.
