The Unique World of Laser Cut Metal Manufacturing

Of all the materials that are requested to be laser cut, metal alloys are at the top of the list. A world where intricate designs and complex shapes can be sculpted from metal with the finesse of a surgeon’s scalpel. This is the realm of laser cutting, a technological marvel that has revolutionized manufacturing. With the precision of a laser beam, metals can be transformed into precision components, supporting numerous industries. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of laser cut metal and discover the endless possibilities it offers. Laser cut metal requests come in from all sectors of industry stemming from established companies to start-ups, seeking their place and advancing technology. There seems to be a never-ending stream of requests for laser cut metal and for service providers, this is a great thing. Technology strives to evolve and by doing so, there is a constant need for support. Laser manufacturing is just one of numerous methods used in manufacturing and by working closely with customers technology continues to move forward using laser cut metal components.
Using laser cutting technology to process metal alloys has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by providing a precise and efficient method for producing precision components. The ability to create intricate shapes and designs with minimal waste has made it a highly sought-after process across a wide range of industries. This versatility is due to the precision and control offered by laser beams, which can be focused to a very small point, allowing for intricate cuts and designs. As a result, industries have gravitated towards laser technology to support a diverse array of applications, from aerospace components to automotive parts and beyond. Each metal alloy does have characteristics that are the best fit for applications and industries. For example, for superior strength to weight ratio, titanium might be the best fit for structural applications. However, titanium is costly, and the application may be better supported by using aluminum. Laser cut metal ideally is going to be processed from rolls or sheets of the various metal alloys. This means that laser cutting metal is focused on processing thin gauges of these alloys. A simple form of this will be a washer type of component, for example with an outer diameter of 50mm and an inner diameter of 30mm. What laser cut metal contributes to this component is high precision, where in many applications, a gasket, shim, or washer are critical in keeping the integrity of flow systems intact. Laser cut metal in general offers versatility that other manufacturing methods do not such as small volume runs, high volume manufacturing, multiple iterations, material usage efficiency, rapid manufacturing, and other unique benefits.
Laser Cut Metal Technology
There are many ways to produce precision components, with each technology having great benefits and attributes when used. With so many options, it may seem difficult to choose which method over another. For laser cut metal, the options center around the laser technologies and what each offer to precision manufacturing. The pages throughout this website offer detailed information of the various laser technologies and the metal alloys used often in industry. The following is an overview of the technology used in laser cutting metal:
| Laser System | Technology | Metal Alloys Processed | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber | High Power, Beam diameters from 18um on up. Accuracy +/- 0.0508mm | Aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, tungsten, copper, brass, nickel | Precision parts for medical, aerospace, automotive |
| CO2 | Power fluctuates- High power used for cutting metals. Accuracy +/- 0.100mm | Steel, stainless steel. Low powered to moderate used for cutting plastics. | Industrial uses for thicker cut metal when high powered CO2 laser are used. |
| Infrared | Power ranges from low to. Beam diameters from 35um . Accuracy +/- 0.0508mm. | Cuts stainless steel alloys from thickness ranging from 0.127mm to 0.635mm. | Precision parts for shims, springs, spacers, etc. medical, electronics, battery energy. |
| Ultraviolet | Low to mid power levels. Accuracy from +/- 0.0127mm . Beam diameter can be 20um. | Cut metal alloy foils from 0.0127mm on up to 0.100 mm thick. Stainless steel, copper, nickel, aluminum. | Microelectronics, optics, battery energy for mesh membranes, gaskets, spacers, heat shields. |
| Pico Second | Accuracy +/- 1-3 microns. Power range depends on the system. Low heat affected zone or HAZ on material, slower cutting. | Best for cutting thin foils like Ultraviolet systems of copper, aluminum, stainless steel, titanium. | Microelectronic machining. Applications where metal cannot have any HAZ . |
| Femto Second | Very accurate and measured in nanometers. Short pulse rate has no heat affected zones or HAZ. | Limited thickness from 0.0254mm to 0.0762mm. Nickel, stainless steel, and others. | Microelectronic machining. Applications where metal foil cannot have any HAZ. |
The Intrigue of Laser Cut Metal
Throughout this website you find detailed information about laser cutting specific alloys like aluminum, copper, tungsten, stainless steel, titanium, and others. Manufacturing precision components out of metal is a fascinating process and listed below are some highlights about the technology:
- Laser Cut Marvels: From cardiac medical devices, textiles support, to dispensing systems used with adhesives, laser cut metal components have proved to be the best method for these applications.
- Material versatility: A wide range of metals, from soft aluminum to hard titanium, and even brazing alloys are processed through laser technology. Some metal foils are thinner than human hair.
- Artistic expression: Laser cutting has become a popular tool for artists and designers, allowing them to create unique and stunning metal sculptures, jewelry, and decorative pieces.
- Research and Development: Many projects start with R&D. Laser cut metal excels at being a versatile tool that mechanical engineers utilize in their research.
- Sustainable manufacturing: Metal alloys can be costly, especially when produced in ultrathin gauges. Using laser technology can reduce waste and improve material efficiency compared to traditional cutting methods, making it a more sustainable option for manufacturing.
- Customizable solutions: Laser cutting technology can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries and applications, making it a versatile and adaptable tool.
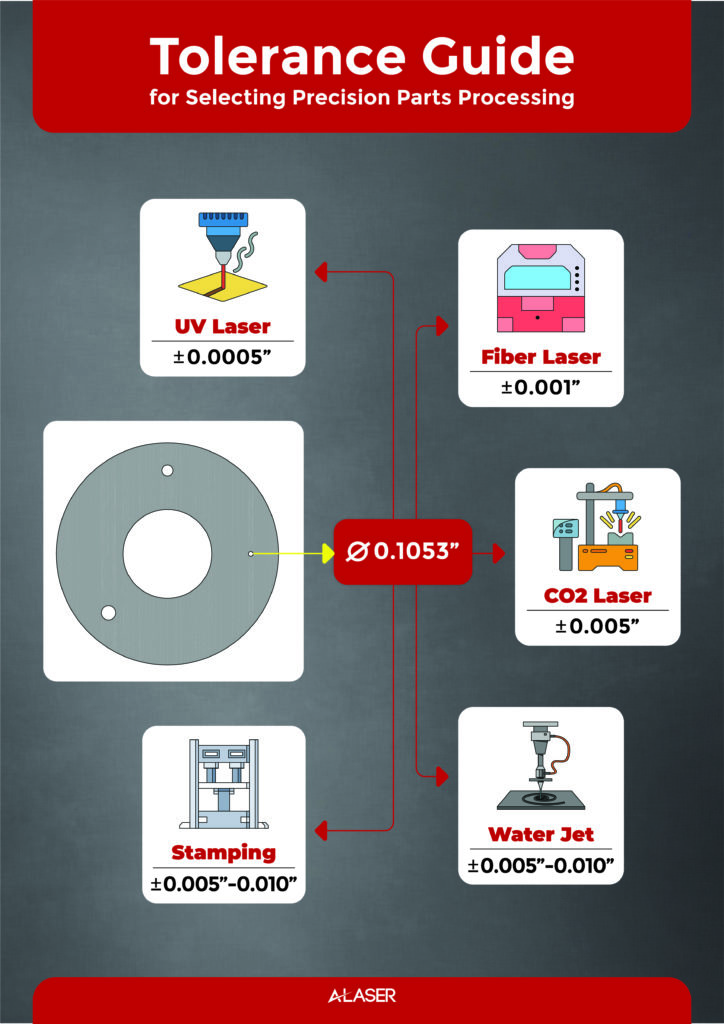
The Tale of Tolerance
You will find throughout this journey into laser cutting technology, that holding a tight tolerance is of vital importance. Metal alloys as described earlier are applied in countless applications and the tolerance to which they are manufactured can mean success or perhaps device failure if the tolerance requirement is not met. By using a beam of intensified light and at focused diameters much smaller than other manufacturing methods, holding a tight tolerance is a great benefit when using laser technology and it is very precise compared to other methods. Tolerance with laser systems is repeatable and once locked in, projects can move from R&D and prototype to high volume manufacturing with no delay. An example of this importance is in the manufacturing of adhesive nozzles. These stainless-steel components are cut in intricate geometries and assembled with multiple parts being the same size. Without adhering to a +/- .001” or 0.0254mm tolerance, the pattern of the nozzles will not project accurately and the manufacturing that these are used for will cease. Laser manufacturing is governed by industry quality standards like ISO 9001 series, which is a system of standards that when followed establish a QMS or Quality Management System. Manufacturers seeking to support laser cut metal projects undergo certification to have the capability that customers require.
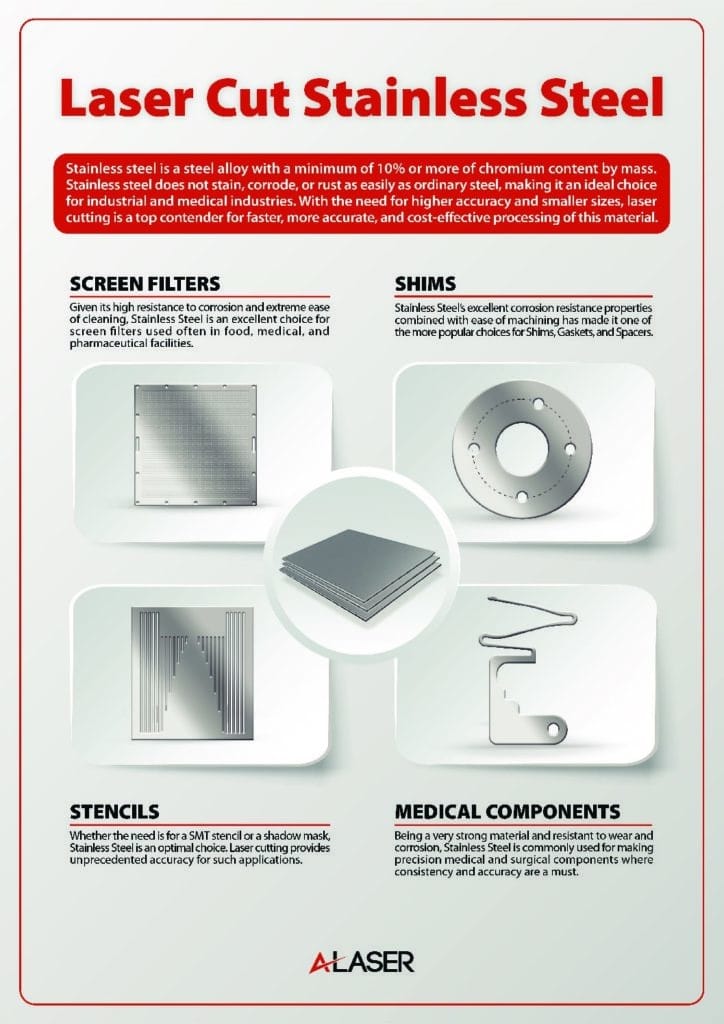
A Testament to Human Ingenuity
As you explore further, you will learn more about laser cut metal components providing support in the medical device industry through cardiac devices, women’s health and diagnostic sequencing. You will see how metal components provide support in aerospace, defense and battery technology. Metal components that assist in the production of textiles and precision components in scientific research and so many other amazing uses. Laser technology, from the precision of its cuts to the versatility of its applications, laser cut metal components have undeniably transformed countless industries. Laser technology itself can create intricate designs, reduce waste, and improve efficiency and by doing so creates an indispensable tool for manufacturers, artists, and engineers alike. As technology continues to advance, we can only imagine the new and exciting possibilities that laser cut metal will unlock in the years to come.
