Laser Cut Theonex Material Service
Trusted by
1,000’s
of Satisfied Customers
30+
Years in Business
Teonex is a polyester related material known as PEN or Polyethylene Naphthalate. This material, made by Toyobo Film Solutions Limited, is used for its higher resistance to heat with anti-hydrolysis and has high mechanical strength than standard polyester or polyimides. Being able to function in harsh environmental conditions, Teonex is used in applications for electrical insulation (as a dielectric), in automotive battery components, and in flexible printed circuits. These and countless other industries rely on materials such as Teonex. To support the need for high precision components, laser technology is a favored partner for critical devices and cutting materials like Teonex, can be a great solution for mechanical applications of flat 2D profiles. With many questions that can come up about laser cutting and particularly of Teonex material, we have provided this series of Q&A and will be happy to answer any additional questions you may have.
What Are the Tightest Tolerances Your Laser Cutting Process Can Maintain When Cutting Teonex?
Laser cutting is synonymous with cutting thin metal foil alloys, but it has a long history of cutting complex polymers and laminated materials for use as simple washers to complex thermal barriers. Cutting materials with laser technology results in precision unmatched by other methods because of the non-contact nature of the process using beam diameters in microns. When cutting Teonex, A-Laser uses UV or ultraviolet systems holding tolerance of +/- 1mil to 2mils for most projects.
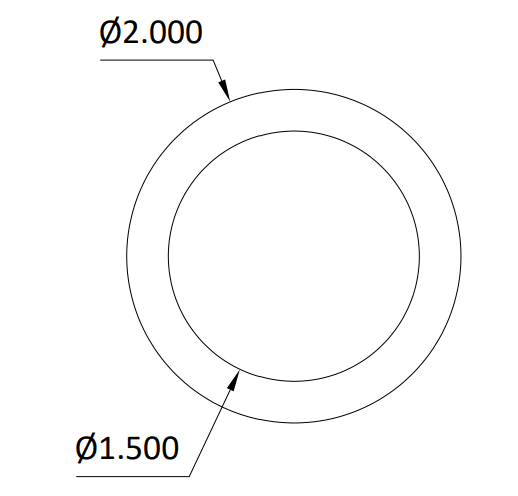
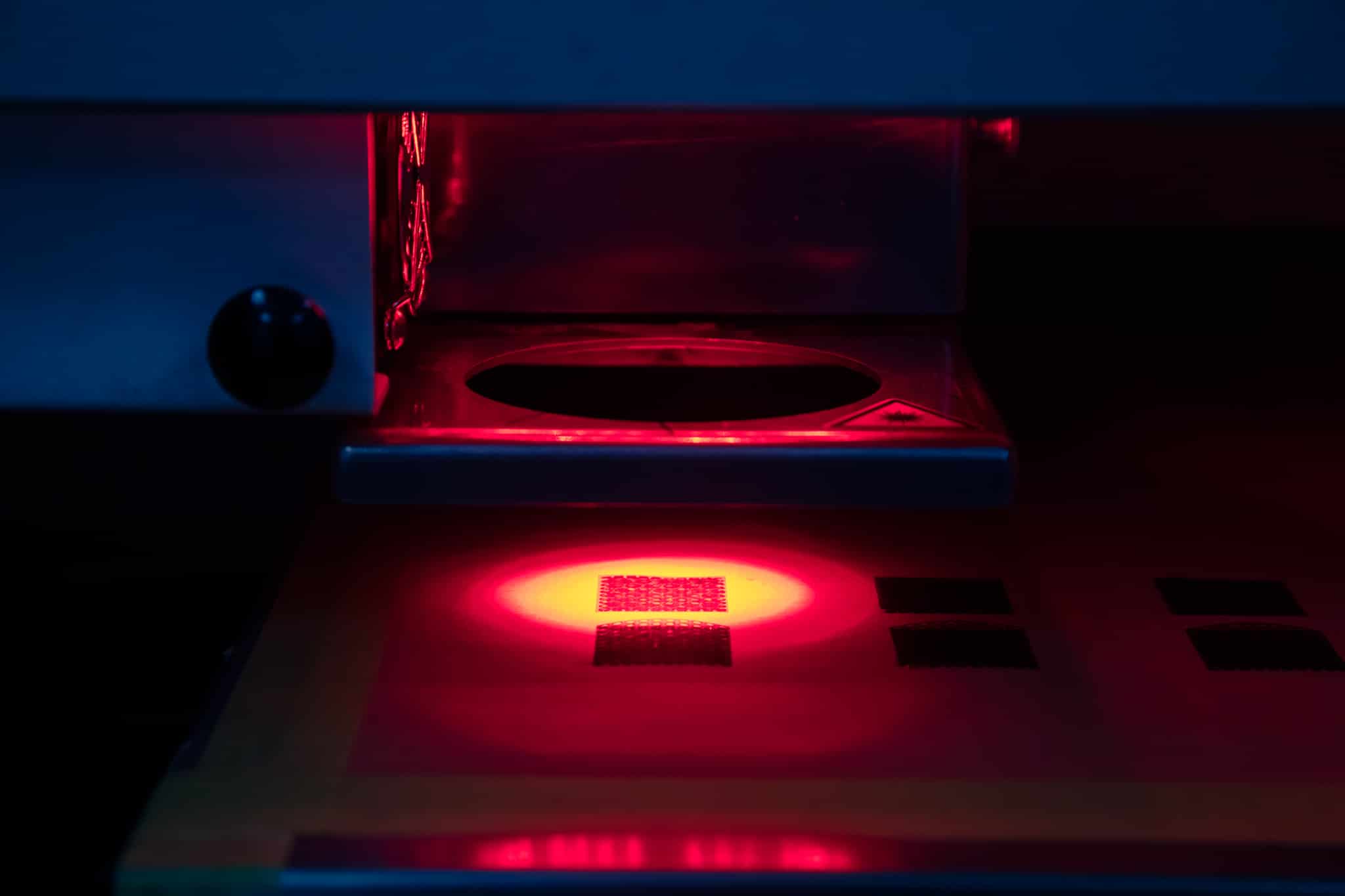
How Does Laser Cutting Compare to Die-cutting, Waterjet, or CNC Machining of Teonex?
You can manufacture numerous different components using the same material, but that’s about the extent a comparison can be fairly done. With so many diverse applications, manufacturing methods focus on capabilities that the technology is best at processing. For example, laser cutting is best at flat, ultra-thin parts within a thickness range of ½ mil to 20 mils for many applications. For metals that range can be up to several millimeters. Die-cutting is best at non-metallics, with simple forms, but manufacturing at a high production rate. Waterjet cutting, excels at thicker materials, by using a combination of water and abrasive media under high pressure. CNC machining, although versatile in using lathes and Mills and drills, is best at removing material from larger blocks or plates. For a thin Teonex, laser would be preferred, but for an enclosure out of aluminum, a CNC machine would be the go to method.


How Do Material Characteristics Like Reflectivity, Softness, or Thermal Conductivity Affect Edge Quality and Tolerance Control in Teonex?
Accurate laser cutting relies on understanding the properties of each material, especially advanced options like Teonex (Polyethylene Naphthalate or PEN) film, valued for its thermal and mechanical strength. With proper management of Teonex’s attributes, we deliver precise edges and tight tolerances for demanding applications.
Thermal Conductivity: Materials like Teonex have a relatively low thermal which during the laser cutting process means the heat generated is concentrated on the cut area minimizing the spreading of heat.
Edge Quality and Tolerance Control: With a minimized HAZ (Heat Affected Zone) the cut edge quality is very good. To ensure this, laser parameters are adjusted, and these include the laser cut speed, laser power (in WATTS), laser passes or cycles, laser frequency and others.
Reflectivity: Teonex absorption of the laser’s wavelength means minimum reflection and higher efficiency in the cutting process, unlike metal substrates that reflect more energy and reduce efficiency and increase the duration of the cut.
Softness: While Teonex is a high-strength film with a high degree of stiffness and dimensional stability (especially its low thermal shrinkage, a benefit over standard PET films), its relative softness compared to ceramics or hard metals means it is prone to melting rather than clean ablation if parameters aren’t optimized.
By recognizing Teonex’s low thermal conductivity, good laser absorption, and dimensional stability, we adjust our laser parameters to optimize performance and reduce thermoplastic risks.
What Edge Quality Can Be Expected When Laser Cutting Teonex? Are Burrs or Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ) Present?
Cutting thermoplastics like Teonex can challenging due to the ablation process producing micro burrs and molten slag if the laser parameters are not ideal. Through years of experience in cutting thermos plastics and thermos interface materials, (TIMS), A-Laser’s team makes adjustments from review of the F.A. or First Article. This procedure is embedded for all projects to undergo. With refinement parameters called the “laser Tool”, very high edge quality is achieved.

What Are the Benefits of Laser Cutting Teonex material?
Laser cutting Teonex provides superior precision and unmatched edge quality because it’s a non-contact, digitally controlled process that minimizes the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ), preventing material stress, warping, and burrs. This technique allows for the creation of highly intricate geometries and tight dimensional tolerances essential for high-performance applications. Furthermore, laser cutting offers significant production benefits, including high processing speed, rapid prototyping due to the absence of costly physical tooling, and efficient material utilization by minimizing the cutting kerf.
