Laser Cut Indium Service
Trusted by
1,000’s
of Satisfied Customers
30+
Years in Business
Indium alloy is one of those materials that is not readily known, but it is used in some very critical applications. In 1863 German chemists Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Richter, discovered Indium, but it was not until 1924 that commercial use of it was applied to add it to other non-ferrous metal alloys. By doing so, the alloys were strengthened and hardened. Ball bearings for aircraft engines were just one of the examples that benefited greatly from early use. The formation of Indium comes as a byproduct of processing zinc. This casting process uses more material, so another process called powder metallurgy is used as a more efficient method. One of the characteristics of Indium is having a low melting point, which has made it a valued choice for temperature bonding applications. For components, Indium foils and thin sheets can be laser cut in precise profiles for use in electronics for thermal interface applications, for solder preforms, for gaskets and seals and for ultra-high vacuum applications and other critical uses. As laser cut Indium may be a new idea and opportunity, the following questions and answers are provided.
Accurately Made
What Are the Tightest Tolerances Your Laser Cutting Process Can Maintain When Cutting Indium?
Our laser cutting process can maintain exceptional tolerances when working with Indium, a soft and malleable metal. We can consistently achieve a tolerance of +/- 1mil to 2mils. What this means for your project is achieving such tight tolerances that are crucial for applications is available today. High precision laser cut Indium maintains tight tolerances and ensures that your components will meet the exact specifications needed for their intended function, guaranteeing a reliable and precise outcome every time.

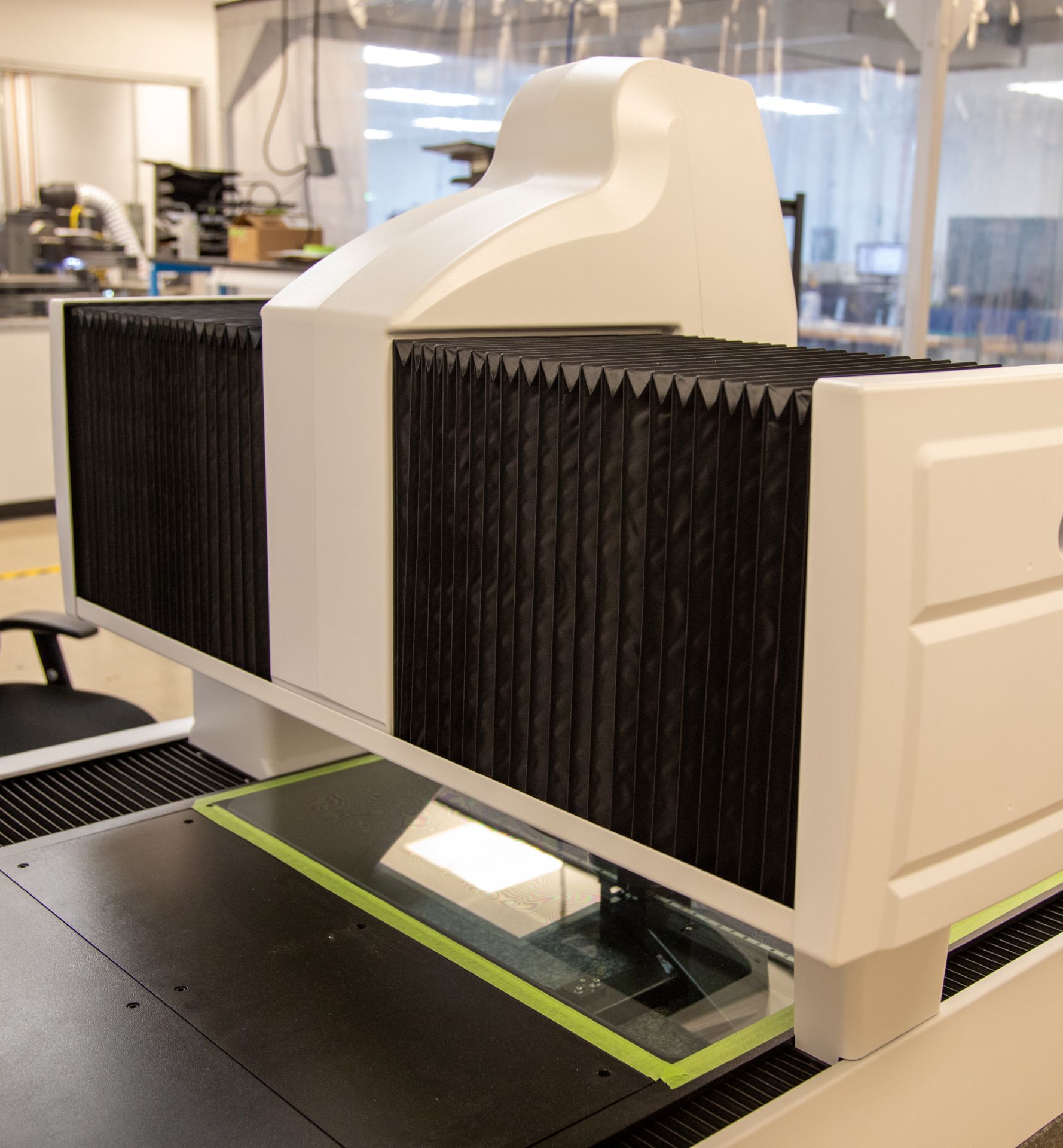
Manufacturing Using Indium
How Does Laser Cutting Compare to Die-cutting, Waterjet, or CNC Machining of Indium?
Manufacturing is a remarkable industry and laser cutting being an option with considerable capabilities, offers engineering teams greater flexibility in designs. It is important, however, to keep in mind that other methods have positive aspects, and each have their own strengths to industries as solutions. The following table is a glimpse of methods in processing Indium alloys.
| Process | Precision & Tolerances | Edge Quality | Material Impact | Speed & Efficiency | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Very High- Micron level possible. | Clean edges, minimal burrs, small HAZ, (heat affected zone). | Non-contact, limited distortion, controlled heat. | Fast for prototypes & small-to-medium runs. | Thin foils, intricate shapes, fine features. |
| Die-Cutting | Moderate- tool wear affects consistency. | Smooth, but edges can deform under pressure. | Mechanical force may distort soft Indium. | High speed for volume production. | Simple, repeated shapes in thin sheets. |
| Waterjet Cutting | Good precision but challenging for soft and thin materials. | No heat-affected zone, edges may be rough. | Cold process avoids melting; risk of edge taper. | Slower setup, moderate cutting speed. | Thicker Indium parts where no heat is allowed. |
| CNC Machining | Good precision, tool size can limit features. | Edges may show tool marks, risk of burrs. | Mechanical stress, potential smearing of soft metal. | Slower, less efficient for thin foils. | Complex 3D parts, thicker Indium components. |
Indium Traits
How Do Material Characteristics Like Reflectivity, Softness, or Thermal Conductivity Affect Edge Quality and Tolerance Control in Indium?
Indium’s softness means it can easily deform under mechanical cutting, so non-contact laser methods are preferred for maintaining tight tolerances. Its relatively low reflectivity allows lasers to cut efficiently, reducing wasted energy compared to highly reflective metals. However, its high thermal conductivity can spread heat quickly, creating small heat-affected zones if not tightly controlled. Together, these traits make precision cutting possible but require optimized laser settings to ensure clean edges and accurate part dimensions.
Laser Cut Edge Quality
What Edge Quality Can Be Expected When Laser Cutting Indium? Are Burrs or Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ) Present?
Laser technology is an excellent method for producing challenging and precise designs out of many different materials. The same is true when cutting Indium in which the outcome produces smooth and precise edges with very little need for post-processing. Burr formation is minimal compared to mechanical methods, thanks to the non-contact nature of the laser. A small heat-affected zone (HAZ) may be present due to Indium’s high thermal conductivity, but with controlled parameters it remains narrow and does not compromise part accuracy or integrity.

Points To Consider
What Are the Benefits of Laser Cutting Indium?
Highlighting benefits of a manufacturing process like laser cutting technology is always a fun thing to do, especially when creating components out of Indium alloy. You can expect clean edges, but caution and care must be taken due to its soft and easily deformed nature. Mechanical stress of die-cutting or machining is avoided, preserving dimensional accuracy even in thin foils. The laser process also supports intricate geometries, rapid prototyping, and consistent results without tool wear. Overall, laser cutting offers efficiency, reliability, and superior edge quality compared to traditional methods, but it is not the only method. Each project will have requirements that may be better fit by other manufacturers. This information hopefully has given insight into laser cutting as a solution, but further investigation into your project is recommended and we are happy to answer any questions you may have.
