Laser Cut Cusil Material Service
Trusted by
1,000’s
of Satisfied Customers
30+
Years in Business
The use of brazing is important for many high-technology applications. Brazing is a method of joining metal alloys using a “filler” alloy that is melted into the joint and upon cooling forms a hermetic seat that is very strong. Cusil material is commonly made up as (typically 72% Ag/28% Cu / 28) and supplied as preforms. Preforms are customized shapes of Cusil and other brazing alloys for an exact application of volume. This accuracy requires high precision of the preform and laser cutting machines are a great solution for these types of parts. Using ultraviolet laser technology, Cusil preforms have replaced manual and often less controlled brazing methods, with accuracy and precision that supports high-technology applications. From a laser manufacturing perspective, processing Cusil into these delicate brazing tools are one of the many benefits lasers cutting service has over other methods. For a deeper look into laser cut preforms of Cusil, please review the following Q&A sections. Upon completion, A-Laser welcomes any additional questions you may have.
Why Tolerance Control Is Important
What Are the Tightest Tolerances Your Laser Cutting Process Can Maintain When Cutting Cusil?

Although precision and tolerance are two distinctive principles they are often combined into one entity, with tolerance being the main factor of concern beginning with the question: “What tolerance can your laser hold?” First of all, laser cutting machines are known for their accuracy and being precise. This means that laser cut features will hit the mark repeatedly. Within the confines of the design, the variable placement of the features is tolerance. When cutting materials like Cusil, you can expect a tolerance of +/- .5 mils top +/- 1mil.
Dare To Compare
How Does Laser Cutting Compare to Die-cutting, Waterjet, or CNC Machining of Cusil?
Brazing alloys are ultra-thin with thicknesses of .5mil to 4 mil for many of the projects we cut. The handling of Cusil foils and producing precision preforms is not a process that is fair to compare outside of laser cutting technology. Die-cutting, is great at cutting mid to high volume of simpler shapes and features but would damage the edges of Cusil. Waterjet cutting using high pressure of water and abrasives is a no-go for cutting Cusil and CNC machines would be awesome if blocks of Cusil were needed to be Milled or lathed. With extreme delicate nature of Cusil foils, laser cutting is best to produce preforms.

Characteristically
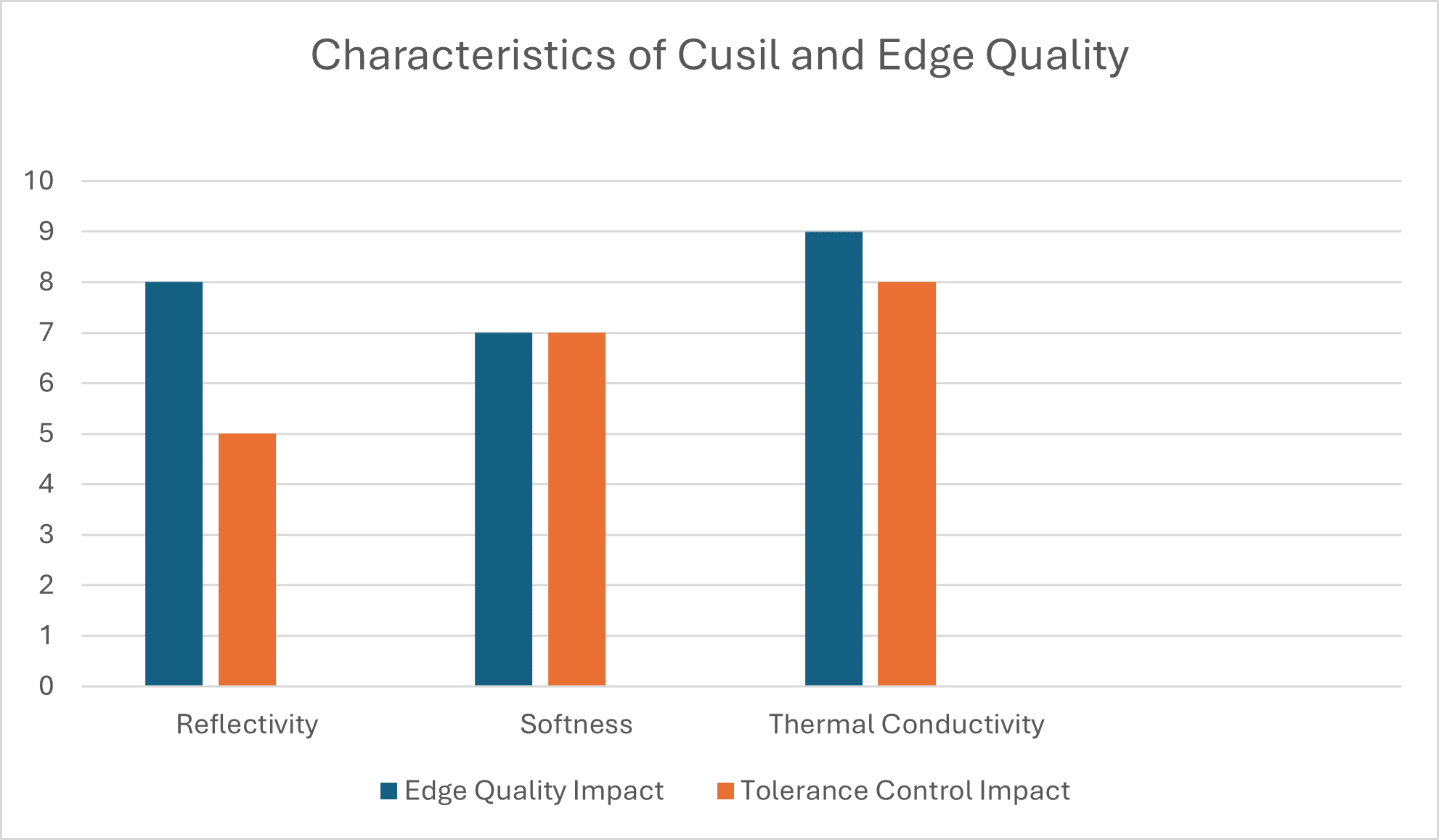
How Do Material Characteristics Like Reflectivity, Softness, or Thermal Conductivity Affect Edge Quality and Tolerance Control in Cusil?
Controlling the laser parameters is the key to achieving optimum edge quality of laser cut Cusil. The bar chart visualizes how reflectivity, softness, and thermal conductivity influence edge quality and tolerance control in Cusil during laser cutting. It clearly shows that reflectivity and thermal conductivity have the strongest overall impact on cutting precision and edge smoothness.
There is a balance between adjusting the laser parameters to meet the degree of edge quality desired while keeping in mind throughput and cost per unit. With qualification of the cut edge by a F.A. or First Article, the dimensional measurement of the profile and features is then adjusted to meet the acceptable criteria set forth in the design.

Reviewing The Cut Edge
What Edge Quality Can Be Expected When Laser Cutting Cusil? Are Burrs or Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ) Present?
Following up on the potential effect of characteristics on edge quality of laser cut Cusil, you can expect a very high degree of quality, with smooth edges and minimal to no slag or burrs off the laser. Preforms of this type are delicate and any post process to remove unwanted slag would easily damage the components.

Key Points to Consider
What Are the Benefits of Laser Cutting Cusil material?
Laser cutting offers a uniquely precise and non-contact method for processing Cusil, a silver–copper alloy prized for its thermal and electrical performance in microelectronic and vacuum applications. Unlike mechanical or abrasive methods, laser cutting delivers tight tolerances, clean, oxide-free edges, and minimal material distortion, even on intricate preforms or thin foils. The high energy density of the laser allows for sharp feature definition while maintaining the alloy’s metallurgical integrity, critical for brazing and bonding applications. For manufacturers of hermetic seals, semiconductor packaging, or thermal interface assemblies, laser-cut Cusil parts provide repeatable accuracy, reduced post-processing, and optimized fit and function translating to higher assembly yields and more reliable component performance.
