Laser Cut Pyralux Service
Trusted by
1,000’s
of Satisfied Customers
30+
Years in Business
If you can imagine combining the characteristics of copper with those of a polyimide, you would have a material with durability, thermal stability, and flexibility. Pyralux is the result of this combination and a key material in manufacturing flexible printed circuit boards or flex PCBs. This copper clad laminate is an essential part of many lightweight, flexible, and reliable circuit boards used in advanced electronics. Examples of Pyralux can be found in applications for medical devices, aerospace where weight is a always a factor.
You will see Pryralux used in consumer electronics and wearable devices, and many more products needing flexible circuitry. Since Pyralux can be damaged by traditional mechanical solutions in PCB assembly, laser cutting technology has become a preferred method in producing the precise geometries that many of these boards have. Often carrying sensitive electronics on these flexible PCBs, laser cutting helps advance these technologies. To give a larger perspective of how laser cutting services support the processing of Pyralux, the following Q&A have been provided.
Laser Accuracy
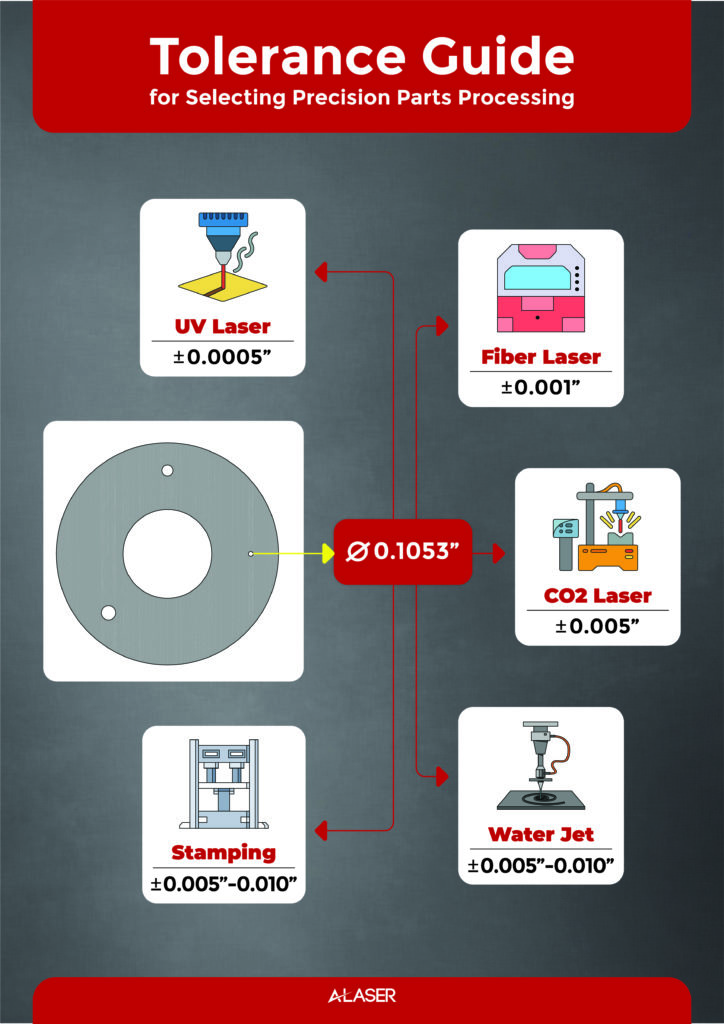
What Are the Tightest Tolerances Your Laser Cutting Process Can Maintain When Cutting Pyralux?
With the use of a UV or ultraviolet laser, you can expect positional accuracy at +/- 1 -2 mils. The beam diameters at 20microm with a 355nm wavelength, offer incredible accuracy for these flexible circuits. This is important because many of these flexible circuits will be placed in a housing or in enclosures that have very little room for error. This accuracy also enables designers to have options that are not possible when using mechanical solutions.

Comparing Different Methods
How Does Laser Cutting Compare to Die-cutting, Waterjet, or CNC Machining of Pyralux?
Pyralux, being a hybrid of copper and polyimide, will respond to different methods of manufacturing in ways that are inherently subjective to the process in use. This really means that though all methods of manufacturing have many positive aspects, not every project is a good fit. For processing Pyralux, the following are some general differences.
- Laser cutting is non-contact, precise, and able to draw curves, microvias, and intricate outlines without blunting a blade. The UV laser’s energy adjusts to both copper and polymer, leaving crisp edges with minimal stress on the flex substrate.
- Die-cutting is more like stamping a cookie cutter through dough. Fast and cost-efficient for high volumes, but it lacks the finesse for micro-scale features or rapid design iterations. It excels in repetition but struggles with complexity.
- Waterjet is brute force with a kind of elegance using a high-pressure stream carving cleanly through thicker metals and composites. But with Pyralux, water and abrasive media can damage the copper-polyimide bond, leaving it overkill for such a delicate laminate.
- CNC machining This method is accurate for rigid boards, but mechanical contact risks tearing thin flex circuits, stressing adhesives, and wearing down tooling. It’s slower for tiny radii and fine features that lasers breeze through.
Laser cut Pyralux with UV technology is a great solution, but the details of every project will determine the best manufacturing solution for your project.
Factoring Characteristics
How Do Material Characteristics Like Reflectivity, Softness, or Thermal Conductivity Affect Edge Quality and Tolerance Control in Pyralux?
The physical characteristics of Pyralux, significantly dictate the success of the cutting tool and the resulting edge quality. Thermal conductivity is key, as the high conductivity of the copper layer can rapidly draw heat away from the cut zone, which requires the cutting tool to deliver precise, controlled energy to avoid incomplete cuts or excessive thermal damage to the adjacent polyimide. Unadjusted laser parameters would lead to a poor edge finish and reduced tolerance control due to charring or a Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ).
Reflectivity is highly relevant for laser cutting, as the copper layer is typically highly reflective, meaning the laser beam’s energy must be precisely managed to be effectively absorbed for clean cutting without damaging or leaving burrs on the softer polyimide. Finally, the softness of the polyimide dielectric compared to the metal layer will require a delicate cutting process like UV laser ablation to achieve tight tolerance control and prevent mechanical distortion, tearing, or burring.
On The Cutting Edge
What Edge Quality Can Be Expected When Laser Cutting Pyralux? Are Burrs or Heat-Affected Zones (HAZ) Present?
The combination of copper and polyimide, such as with Pyralux, has its challenges even for experienced laser service providers. Parameters used for cutting copper and those for cutting polyimide, have to be refined and form a new “laser cutting tool”. By doing this in adjusting the laser power, frequency, speed of travel, and laser passes (cycles), you can expect very high edge quality. There will be some edge color discoloration due to the nature of the ablation and some slight HAZ or heat affected zones. However, in countless procedures, this has not been a factor for concern.


Concluding Notes
What Are the Benefits of Laser Cutting Pyralux?
It is enjoyable to mention the virtues and benefits of laser cutting because we see the results of precise cut materials like Pyralux and how these flex boards or perhaps components made from other materials are part of the success of your project and your product. Laser manufacturing offers more than just precision; it opens the possibilities for design directions that other manufacturing methods cannot support. Laser technology is a rapid method for prototypes, even for evaluation runs of printed circuits. By using this technology, development of key components can be ramped up for production volumes as a member in the supply chain.
