Precision Laser Processing of Exotic Alloys With Ultraviolet Technology
Ultraviolet light is completely invisible to the human eye, but we are aware of its presence when a sunburn occurs. Visible light is made of different wavelengths, and the ultraviolet spectrum lies just beyond the violet end, hence the name ultraviolet or just beyond violet. This wavelength is shorter than visible light but has higher frequencies that give the photons more energy and do react to the environment in ways that react to materials. This is why UV lasers are used for cutting a host of exotic alloys with precision and accuracy not found in different manufacturing methods. Photoablation by UV lasers is the disintegration of the molecular bonds in materials that has lower levels of thermal stress than some other laser cutting methods like fiber and CO2 systems. This characteristic is important to prevent components from excessive HAZ or heat affected zones. UV lasers are the benefactors of technological advancements in electronic sensors, capacitors, resistors, diodes, and mechanical elements such as motors, optics, robotics and many other factors. These highly complex tools use laser precision to cut thin and ultra thin metal alloys in support of a wide range of industries and applications by cutting design profiles that can be challenging to other manufacturing methods. UV lasers have their niche in thin material manufacturing of precision parts with flexibility and repeatable quality for small development projects to being a supplier for high volume production.
Exotic Alloys
This is one of the gleaming characteristics that UV laser technology has, with its ability in cutting or ablation of many alloys. This capability has given many industries the tools for refining their technologies and developing new products. The following list of exotic alloys are just some of the more challenging materials being laser cut.

| Material | Characteristics and applications | Why UV Lasers Are Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel Based Super Alloys | ||
| Inconel | Known for extreme strength and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. | UV lasers provide clean, precise cuts without inducing thermal stress or altering the alloy's critical microstructure. |
| Hastelloy | Highly resistant to corrosion and high temperatures. | |
| Titanium Alloys | ||
| Titanium | Used for its strength and versatility. | UV lasers' cold ablation process avoids thermal stress as compared to other methods. |
| Nitinol | A shape memory alloy and super elastic material, highly flexible and kink resistant. | |
| Cobalt Chrome Alloys | excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility | Similar to titanium, their hardness and sensitivity to thermal effects. UV lasers ensure smooth, cuts with material integrity intact. |
| Refractory Metals | ||
| Tantalum | Highly corrosion-resistant, biocompatible | Their extreme hardness and high melting points make mechanical machining difficult and costly. UV lasers provide the necessary precision and control. |
| Molybdenum | High melting point, good strength and stiffness at high temperatures. | |
| Tungsten | Highest melting point of all metals, very dense and hard. | |
| Precious Metals | ||
| Platinum Iridium | Biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, high density. | For delicate, high-value components where material waste must be minimized and feature sizes are extremely small. |
| Gold | Excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, biocompatible. | |
| Ceramics & Composites | ||
| Alumina Nitride | High thermal conductivity, electrical insulators. | Materials can be brittle and prone to mechanical stress. Thermal lasers can cause delamination or charring in composites. UV lasers provide a precise, stress-free cut. |
| Carbon Fiber | Lightweight, high strength, used in aerospace | |
| Graphene | Pliability and with high thermal range of use. Great for gaskets | |

Why Ultraviolet Lasers?
Ultraviolet lasers are not the only types available for manufacturing and certainly not the only method for producing precision parts. Each laser technology has its own attributes and characteristics that manufacturers use to focus their services. For example, fibers lasers are best at cutting metal alloys, including exotic alloys, but the raw materials need to be in thicker gauges or damage to the alloys can occur. Fiber lasers operate at power levels much greater than UV lasers and use higher power than other laser systems in general and are excellent in cutting many of the same alloys as ultraviolet systems, but at thicker gauges with more robust features. Femtosecond and Picosecond lasers produce extremely fine features of just a few microns in size. This however limits their capability to cut only ultra-thin foils of metal alloys, both exotic and non-exotic types with no heat affected zones. CO2 lasers are the best used to cut non-metallic materials like clear plastics, wood and paper-based substrates. They can be equipped with higher power to cut metals, but these tend to be industry and service specific. For UV lasers, they fill the capability gaps left over from the other laser technologies, becoming a key supplier of precision components from metallic alloys and non-metallic substrates. The versatility of UV lasers is what makes their capabilities a positive factor for countless industries, both in production needs and for product development with R&D and prototyping being foremost in their support. When thinking about using UV laser technology, keep these attributes in mind:
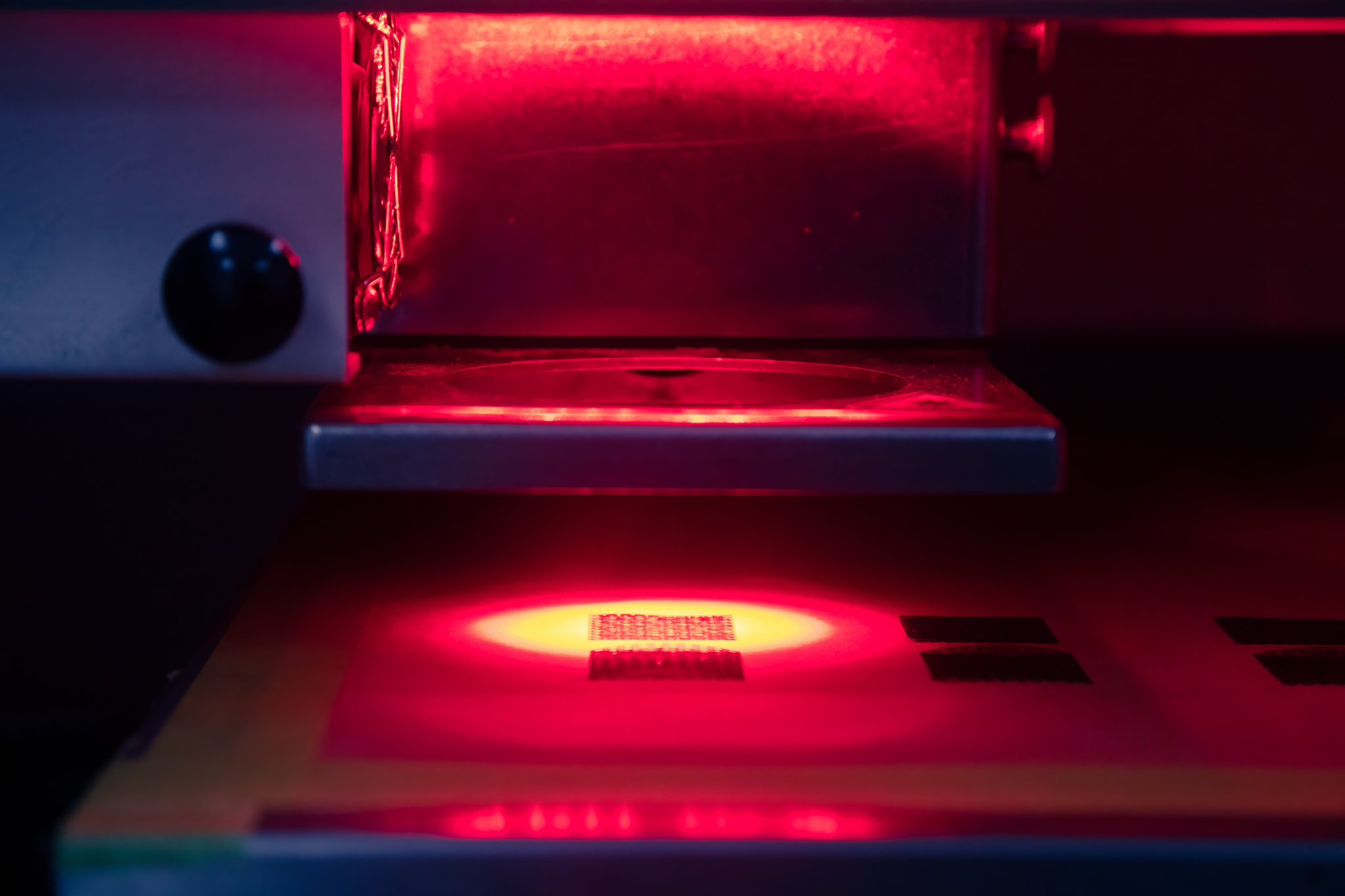
- Clean Edge Processing
- Minimal Heat Affected Zones
- Reduced Material Waste
- Repeatability
- High Quality
- Tight Tolerances

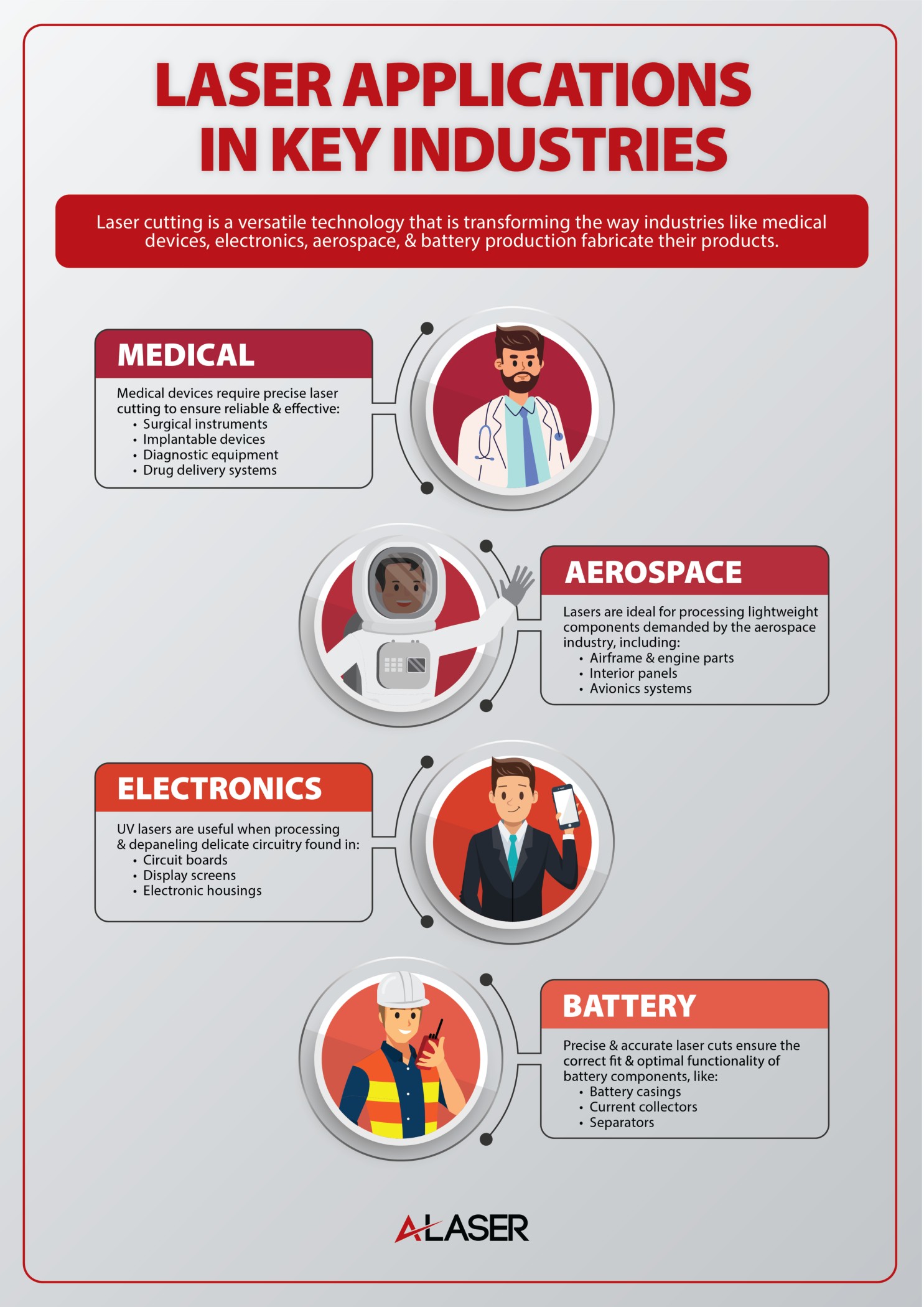
Additionally, the following list of solutions and applications will be a guide to UV laser cutting support:
- Aerospace Laser Cutting
- Defense Laser Cutting
- Miniaturization Solutions
- Prototype laser Cutting
- Microelectronics Manufacturing
- Semiconductor Laser Cutting
- Medical Device Laser Cutting
The list of industries is extensive and applications too numerous to compile, but from these examples, it is clear that UV laser cutting of exotic alloys has become a proven provider of precision parts. The utilization of ultraviolet laser technology for cutting exotic alloys represents a transformative breakthrough, offering unparalleled precision and reliability. This approach addresses vital and critical needs across a spectrum of industries, delivering advanced solutions for intricate product applications. By embracing this technology, industries can not only meet today’s demanding standards but also drive innovation and set the foundation for tomorrow’s advancements. Truly, UV laser cutting has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes and redefine possibilities in sectors such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, and microelectronics.
